Nobody expects scruples from an email phishing attacker. So, it should come as no surprise that these cybercriminals are using the COVID-19 vaccine, a source of hope and maybe even desperate need for millions, as a hook to worm their way into organizations’ systems.
Cybercriminals often prey on the urgency and sensitivity of individuals, using topics and keywords they know will help their emails reach their damaging end goals. These goals include credential harvesting, installing of malware, obtaining additional personally identifiable information (PII) and other outcomes that can harm organizations and individuals alike. We’ve seen this before with attacks that attempt to impersonate organizations’ COVID-19 response communications.
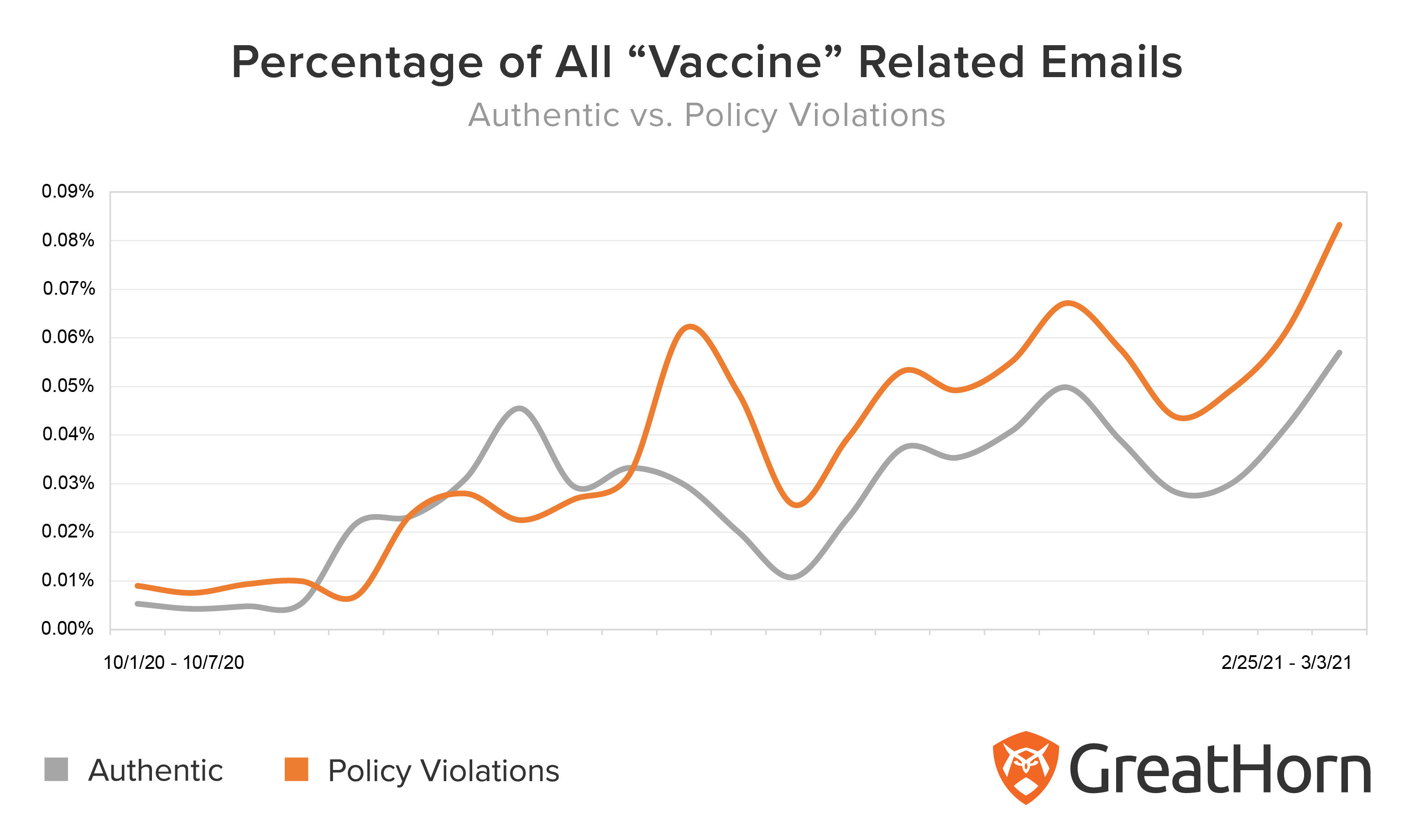
In the past two months, the GreatHorn Threat Intelligence Team has observed a significant increase in the use of the word “vaccine” in phishing attacks, relative to the frequency with which the term is used in authentic emails.
Let’s establish the timeline:
On Dec. 15, 2020, coronavirus vaccinations began in the U.S. Since then, legitimate emails containing the word “vaccine”, or variations of (e.g. vaccination, etc) have increased in frequency. However, in mid-December, cybercriminals began significantly expanding their use of this keyword.
During the week of December 15, 2020, suspicious emails containing the word “vaccine” rose significantly, reaching a point where the quantity of authentic emails was just half that of suspicious emails. Beginning in January 2021, authentic and suspicious emails containing the word “vaccine” continued with the same trend, whereas suspicious emails outpaced authentic emails by greater than 50% of all email delivered. And, in the first week of March 2021 the quantity of suspicious emails had doubled in quantity since the January 2021.
Of course, users in your organization wouldn’t be expected to stop opening emails about COVID-19 vaccinations. Companies have important information to communicate to their employees about return-to-work schedules and ways they are keeping employees safe.
However, suspicious emails can be flagged or filtered by other means, even if it’s a matter as simple as identifying that a sender name or domain looks like one that the user frequently corresponds with, but isn’t. GreatHorn is designed to alert your users when an email may be legitimate, but has something phishy about it that merits their close attention, before opening the email or clicking a link.
Example Vaccine-Related Phish
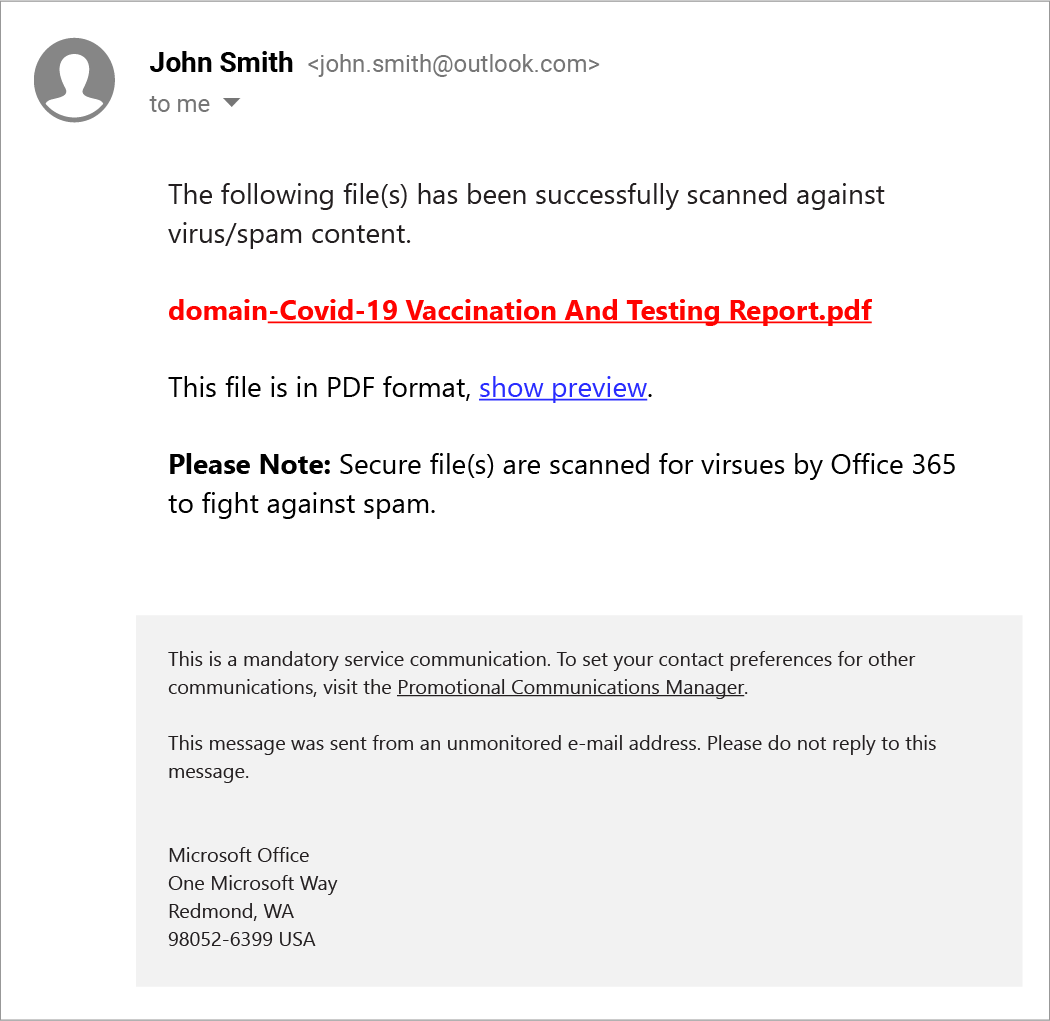
Step 1: An email is delivered that links to a pdf, purportedly a vaccination report.
The templated message after the call-to-action informs the user that “secure files are scanned for viruses by Office 365 to fight against spam.” This kind of detail, which mimics standard email security practices, is a common tactic used by cybercriminals, designed to give users a false sense of security. In this case, it also further sets expectations for Office 365 in Step 2.
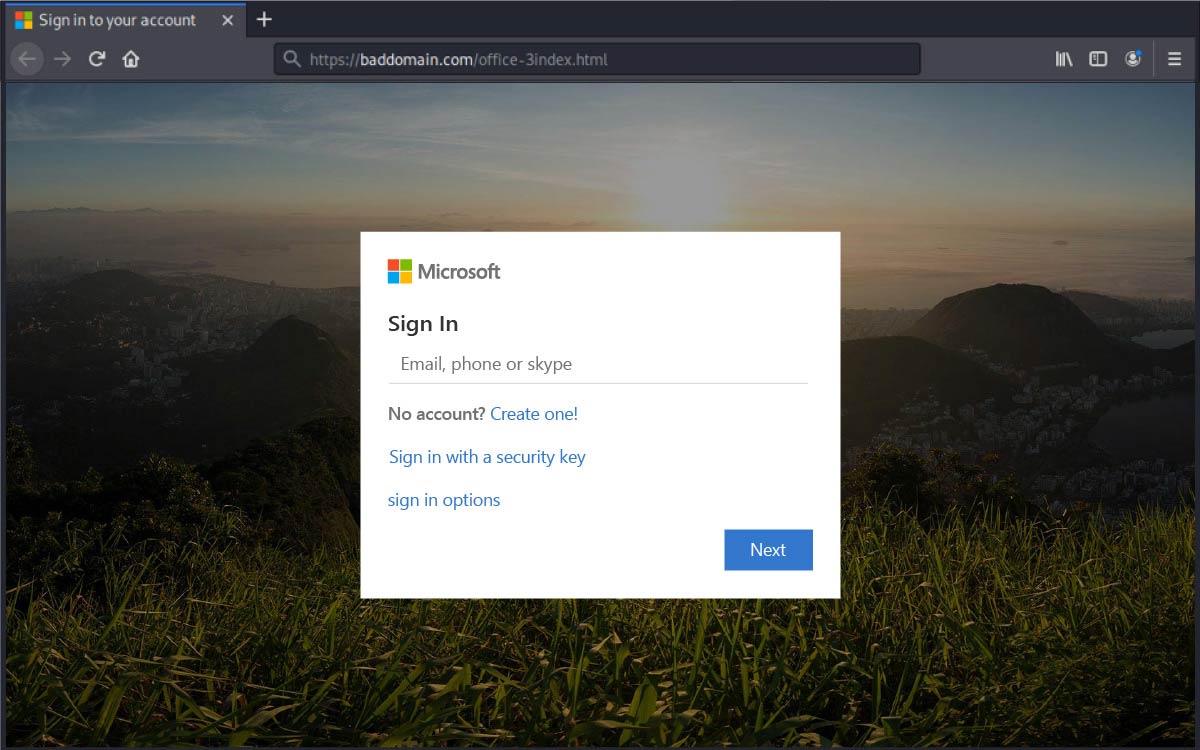
Step 2: The user is asked to log into their Microsoft Office 365 account.
Following the prior step, which set an expectation that an Office 365 account would be required, this next step appears like a standard log-in or authentication to gain access to information.
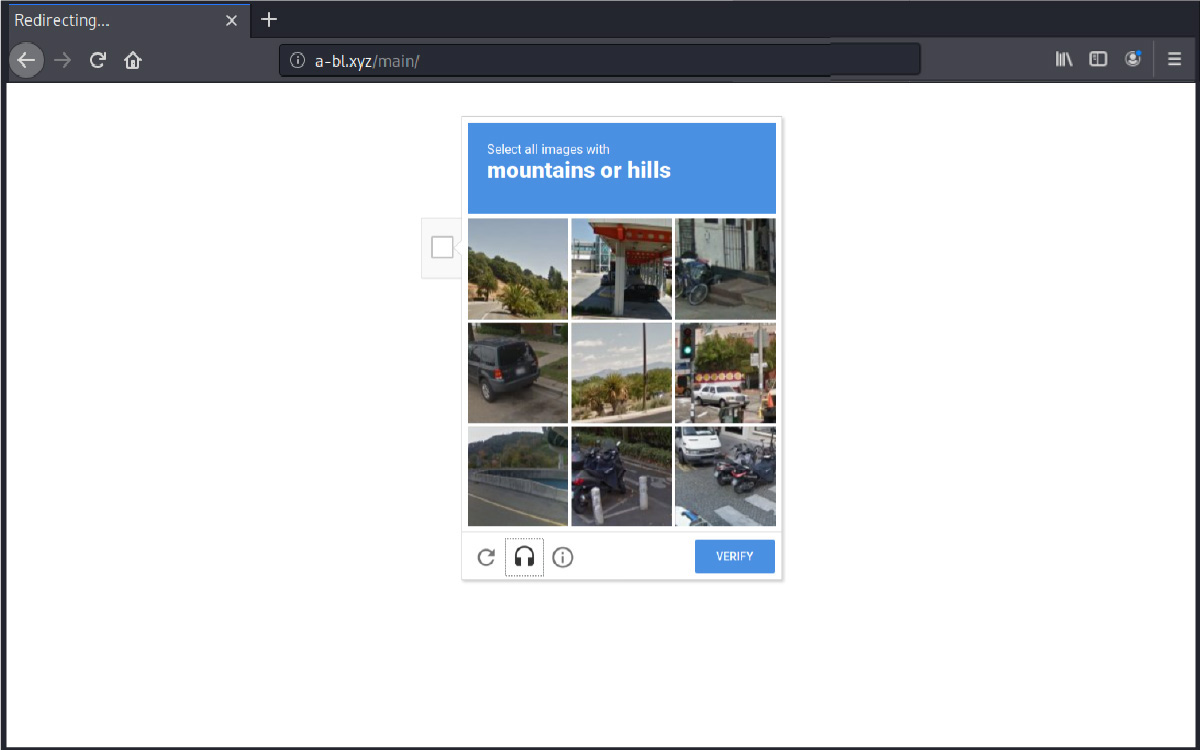
Step 3: reCAPTCHA
Taking the security theater a little further, the cybercriminals employ a more sophisticated tactic. This reCAPTCHA page, designed to emulate a legitimate security step employed on many websites, is intended to further lull the user into a sense the interaction is secure and normal.
If the user then enters both their username and password, they’ll be providing scammers with their login credentials. The attackers can then gain access to the recipient’s email contact lists and other sensitive data, including cloud storage.
While cybercriminals continue to prey on relevant and often urgent topics it becomes more difficult to detect and remediate the threats targeting your organization and users. Being able to analyze URLs, leverage machine vision to identify credential harvesting attempts, and understand historic communication patterns between senders and recipients becomes critical to maintaining control over your organization’s data and systems. GreatHorn’s Advanced Threat Detection is your partner to reduce your time to detect and respond to these advanced phishing attacks.




